Introduction to Data Structures
Last Updated :
16 Apr, 2024
What is Data Structure?
A data structure is a particular way of organising data in a computer so that it can be used effectively. The idea is to reduce the space and time complexities of different tasks.
The choice of a good data structure makes it possible to perform a variety of critical operations effectively. An efficient data structure also uses minimum memory space and execution time to process the structure. A data structure is not only used for organising the data. It is also used for processing, retrieving, and storing data. There are different basic and advanced types of data structures that are used in almost every program or software system that has been developed. So we must have good knowledge of data structures.
Need Of Data Structure:
The structure of the data and the synthesis of the algorithm are relative to each other. Data presentation must be easy to understand so the developer, as well as the user, can make an efficient implementation of the operation.
Data structures provide an easy way of organising, retrieving, managing, and storing data.
Here is a list of the needs for data.
- Data structure modification is easy.
- It requires less time.
- Save storage memory space.
- Data representation is easy.
- Easy access to the large database
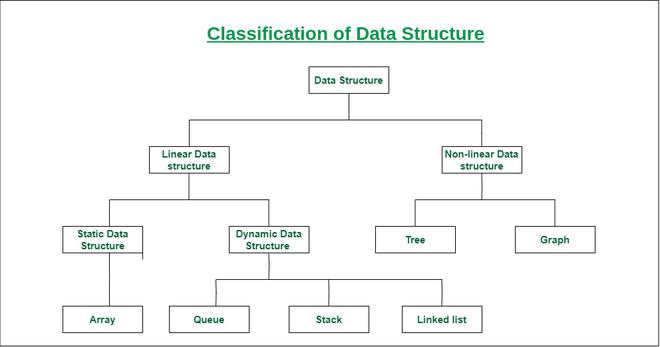
- Linear Data Structure
- Non-Linear Data Structure.
Linear Data Structure:
- Elements are arranged in one dimension ,also known as linear dimension.
- Example: lists, stack, queue, etc.
Non-Linear Data Structure
- Elements are arranged in one-many, many-one and many-many dimensions.
- Example: tree, graph, table, etc.
Most Popular Data Structures:
An array is a collection of data items stored at contiguous memory locations. The idea is to store multiple items of the same type together. This makes it easier to calculate the position of each element by simply adding an offset to a base value, i.e., the memory location of the first element of the array (generally denoted by the name of the array).

Array Data Structure
Like arrays, Linked List is a linear data structure. Unlike arrays, linked list elements are not stored at a contiguous location; the elements are linked using pointers.
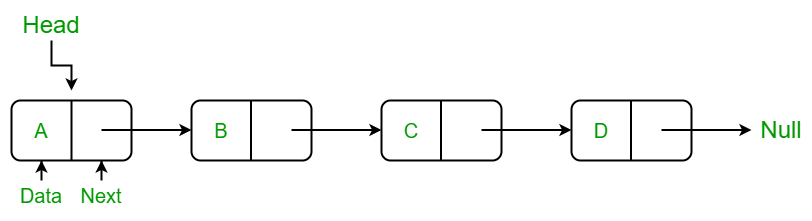
Linked Data Structure
Stack is a linear data structure which follows a particular order in which the operations are performed. The order may be LIFO(Last In First Out) or FILO(First In Last Out). In stack, all insertion and deletion are permitted at only one end of the list.
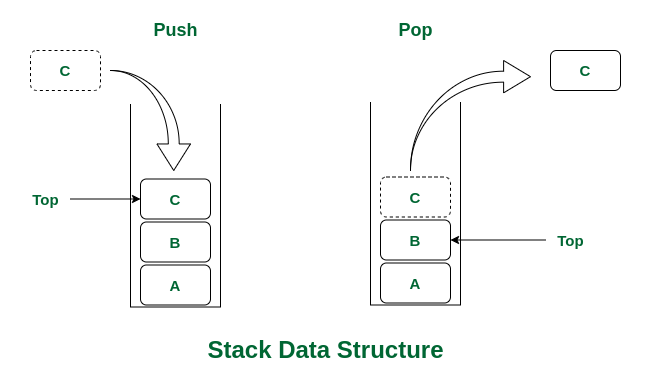 Stack Operations:
Stack Operations:
- push(): When this operation is performed, an element is inserted into the stack.
- pop(): When this operation is performed, an element is removed from the top of the stack and is returned.
- top(): This operation will return the last inserted element that is at the top without removing it.
- size(): This operation will return the size of the stack i.e. the total number of elements present in the stack.
- isEmpty(): This operation indicates whether the stack is empty or not.
Like Stack, Queue is a linear structure which follows a particular order in which the operations are performed. The order is First In First Out (FIFO). In the queue, items are inserted at one end and deleted from the other end. A good example of the queue is any queue of consumers for a resource where the consumer that came first is served first. The difference between stacks and queues is in removing. In a stack we remove the item the most recently added; in a queue, we remove the item the least recently added.
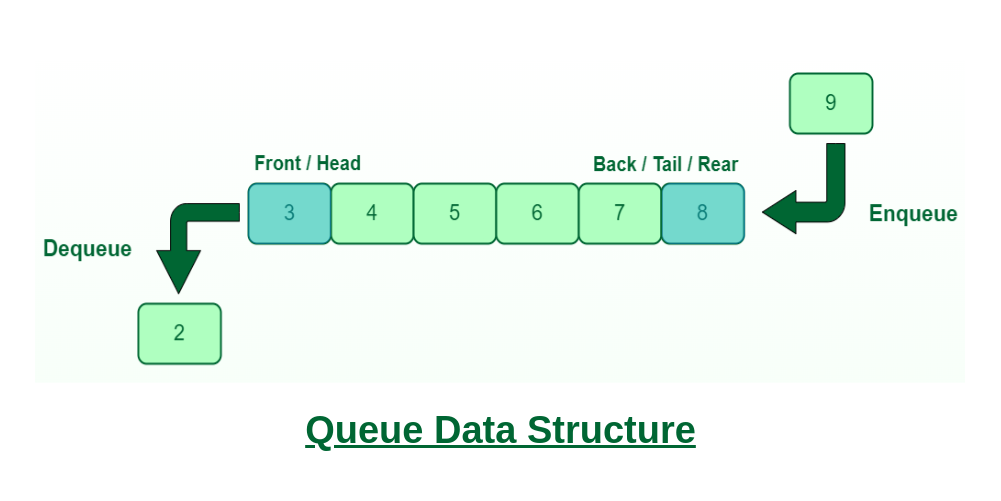
Queue Data Structure
Queue Operations:
- Enqueue(): Adds (or stores) an element to the end of the queue..
- Dequeue(): Removal of elements from the queue.
- Peek() or front(): Acquires the data element available at the front node of the queue without deleting it.
- rear(): This operation returns the element at the rear end without removing it.
- isFull(): Validates if the queue is full.
- isNull(): Checks if the queue is empty.
Unlike Arrays, Linked Lists, Stack and queues, which are linear data structures, trees are hierarchical data structures. A binary tree is a tree data structure in which each node has at most two children, which are referred to as the left child and the right child. It is implemented mainly using Links.
A Binary Tree is represented by a pointer to the topmost node in the tree. If the tree is empty, then the value of root is NULL. A Binary Tree node contains the following parts.
1. Data
2. Pointer to left child
3. Pointer to the right child

Binary Tree Data Structure
A Binary Search Tree is a Binary Tree following the additional properties:
- The left part of the root node contains keys less than the root node key.
- The right part of the root node contains keys greater than the root node key.
- There is no duplicate key present in the binary tree.
A Binary tree having the following properties is known as Binary search tree (BST).
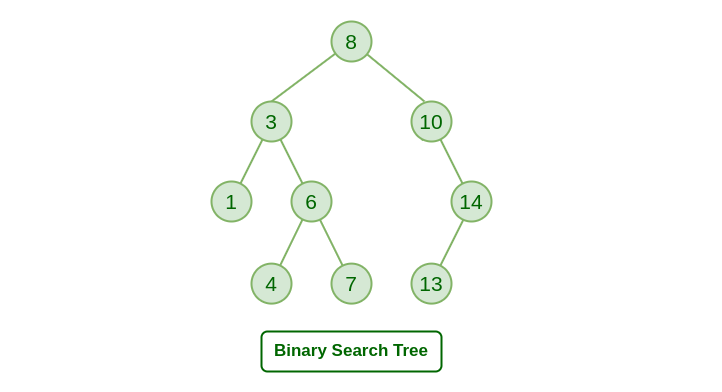
Binary Search Tree Data Structure
A Heap is a special Tree-based data structure in which the tree is a complete binary tree. Generally, Heaps can be of two types:
- Max-Heap: In a Max-Heap the key present at the root node must be greatest among the keys present at all of its children. The same property must be recursively true for all sub-trees in that Binary Tree.
- Min-Heap: In a Min-Heap the key present at the root node must be minimum among the keys present at all of its children. The same property must be recursively true for all sub-trees in that Binary Tree.
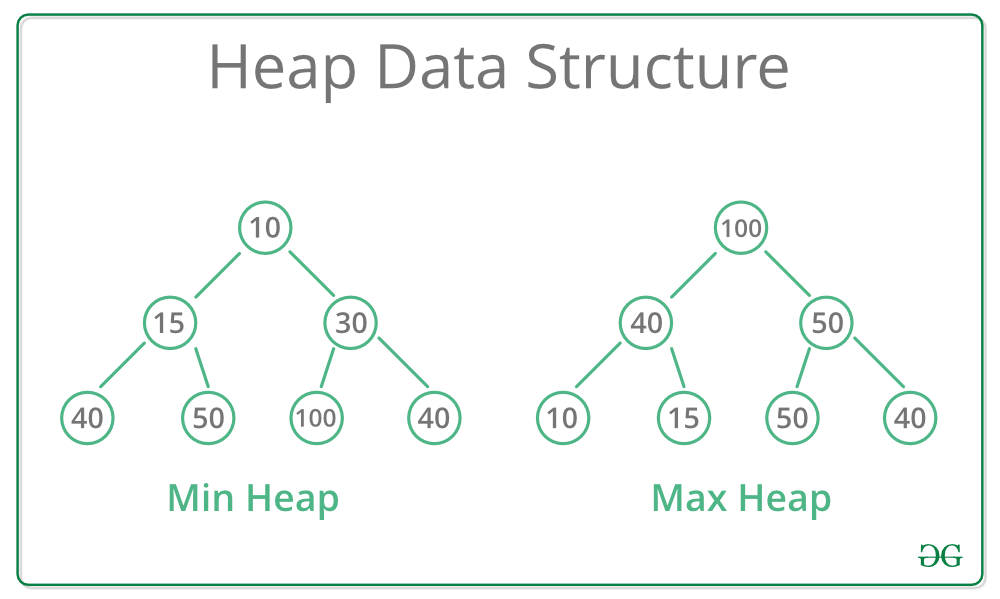
Max and Min Heap
Hashing is an important Data Structure which is designed to use a special function called the Hash function which is used to map a given value with a particular key for faster access of elements. The efficiency of mapping depends on the efficiency of the hash function used.
Let a hash function H(x) maps the value x at the index x%10 in an Array. For example, if the list of values is [11, 12, 13, 14, 15] it will be stored at positions {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} in the array or Hash table respectively.

Hash Data Structure
A matrix represents a collection of numbers arranged in an order of rows and columns. It is necessary to enclose the elements of a matrix in parentheses or brackets.
A matrix with 9 elements is shown below.

Matrix
Trie is an efficient information retrieval data structure. Using Trie, search complexities can be brought to an optimal limit (key length). If we store keys in the binary search tree, a well-balanced BST will need time proportional to M * log N, where M is maximum string length and N is the number of keys in the tree. Using Trie, we can search the key in O(M) time. However, the penalty is on Trie storage requirements.
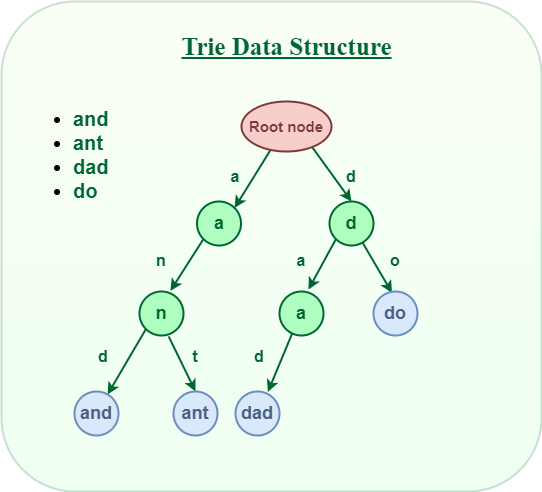
Trie Data Structure
Graph is a data structure that consists of a collection of nodes (vertices) connected by edges. Graphs are used to represent relationships between objects and are widely used in computer science, mathematics, and other fields. Graphs can be used to model a wide variety of real-world systems, such as social networks, transportation networks, and computer networks.

Graph Data Structure
Applications of Data Structures:
Data structures are used in various fields such as:
- Operating system
- Graphics
- Computer Design
- Blockchain
- Genetics
- Image Processing
- Simulation,
- etc.
Please Login to comment...