The For Loops in Python are a special type of loop statement that is used for sequential traversal. Python For loop is used for iterating over an iterable like a String, Tuple, List, Set, or Dictionary.
In Python, there is no C style for loop, i.e., for (i=0; I <n; i++). The For Loops in Python is similar to each loop in other languages, used for sequential traversals.
Flowchart of Python For Loop
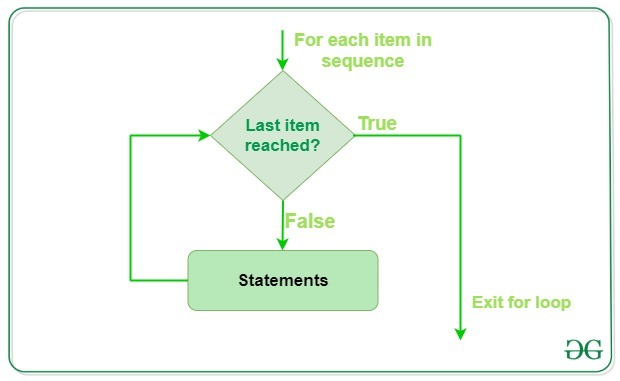
For Loop flowchart
How to use the for loop in Python
In Python, the for loop is used to iterate over a sequence (such as a list, tuple, string, or dictionary) or any iterable object. The basic syntax of the for loop is:
Python For Loop Syntax
for var in iterable:
# statements
Note: In Python, for loops only implement the collection-based iteration.
Here we will see Python for loop examples with different types of iterables:
Python For Loop with String
This code uses a for loop to iterate over a string and print each character on a new line. The loop assigns each character to the variable i and continues until all characters in the string have been processed.
Python
# Iterating over a String
print("String Iteration")
s = "Geeks"
for i in s:
print(i)
Output:
String Iteration
G
e
e
k
s
Python for loop with Range
This code uses a Python for loop with index in conjunction with the range() function to generate a sequence of numbers starting from 0, up to (but not including) 10, and with a step size of 2. For each number in the sequence, the loop prints its value using the print() function. The output will show the numbers 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8.
Python
for i in range(0, 10, 2):
print(i)
Output :
0
2
4
6
8
Python for loop Enumerate
In Python, the enumerate() function is used with the for loop to iterate over an iterable while also keeping track of the index of each item.
Python
l1 = ["eat", "sleep", "repeat"]
for count, ele in enumerate(l1):
print (count, ele)
Output
0 eat
1 sleep
2 repeat
Nested For Loops in Python
This code uses nested for loops to iterate over two ranges of numbers (1 to 3 inclusive) and prints the value of i and j for each combination of the two loops. The inner loop is executed for each value of i in the outer loop. The output of this code will print the numbers from 1 to 3 three times, as each value of i is combined with each value of j.
Python
for i in range(1, 4):
for j in range(1, 4):
print(i, j)
Output :
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 1
2 2
2 3
3 1
3 2
3 3
Python For Loop Over List
This code uses a for loop to iterate over a list of strings, printing each item in the list on a new line. The loop assigns each item to the variable I and continues until all items in the list have been processed.
Python
# Python program to illustrate
# Iterating over a list
l = ["geeks", "for", "geeks"]
for i in l:
print(i)
Output :
geeks
for
geeks
Python for loop in One Line
Python
Numbers =[x for x in range(11)]
print(Numbers)
Output
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
Python For Loop with Dictionary
This code uses a for loop to iterate over a dictionary and print each key-value pair on a new line. The loop assigns each key to the variable i and uses string formatting to print the key and its corresponding value.
Python
# Iterating over dictionary
print("Dictionary Iteration")
d = dict()
d['xyz'] = 123
d['abc'] = 345
for i in d:
print("% s % d" % (i, d[i]))
Output:
Dictionary Iteration
xyz 123
abc 345
Python For Loop with Tuple
This code iterates over a tuple of tuples using a for loop with tuple unpacking. In each iteration, the values from the inner tuple are assigned to variables a and b, respectively, and then printed to the console using the print() function. The output will show each pair of values from the inner tuples.
Python
t = ((1, 2), (3, 4), (5, 6))
for a, b in t:
print(a, b)
Output :
1 2
3 4
5 6
Python For Loop with Zip()
This code uses the zip() function to iterate over two lists (fruits and colors) in parallel. The for loop assigns the corresponding elements of both lists to the variables fruit and color in each iteration. Inside the loop, the print() function is used to display the message “is” between the fruit and color values. The output will display each fruit from the list of fruits along with its corresponding color from the colours list.
Python
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
colors = ["red", "yellow", "green"]
for fruit, color in zip(fruits, colors):
print(fruit, "is", color)
Output :
apple is red
banana is yellow
cherry is green
Control Statements that can be used with For Loop in Python
Loop control statements change execution from their normal sequence. When execution leaves a scope, all automatic objects that were created in that scope are destroyed. Python supports the following control statements.
Continue in Python For Loop
Python continue Statement returns the control to the beginning of the loop.
Python
# Prints all letters except 'e' and 's'
for letter in 'geeksforgeeks':
if letter == 'e' or letter == 's':
continue
print('Current Letter :', letter)
Output:
Current Letter : g
Current Letter : k
Current Letter : f
Current Letter : o
Current Letter : r
Current Letter : g
Current Letter : k
Break in Python For Loop
Python break statement brings control out of the loop.
Python
for letter in 'geeksforgeeks':
# break the loop as soon it sees 'e'
# or 's'
if letter == 'e' or letter == 's':
break
print('Current Letter :', letter)
Output:
Current Letter : e
For Loop in Python with Pass Statement
The pass statement to write empty loops. Pass is also used for empty control statements, functions, and classes.
Python
# An empty loop
for letter in 'geeksforgeeks':
pass
print('Last Letter :', letter)
Output:
Last Letter : s
For Loops in Python with Else Statement
Python also allows us to use the else condition for loops. The else block just after for/while is executed only when the loop is NOT terminated by a break statement.
Python
# Python program to demonstrate
# for-else loop
for i in range(1, 4):
print(i)
else: # Executed because no break in for
print("No Break\n")
Output:
1
2
3
No Break
Python For Loop Exercise Questions
Below are two Exercise Questions on Python for-loops. We have covered continue statement and range() function in these exercise questions.
Q1. Code to implement Continue statement in for-loop
Python
clothes = ["shirt", "sock", "pants", "sock", "towel"]
paired_socks = []
for item in clothes:
if item == "sock":
continue
else:
print(f"Washing {item}")
paired_socks.append("socks")
print(f"Washing {paired_socks}")
Output
Washing shirt
Washing pants
Washing towel
Washing ['socks']
Q2. Code to implement range function in for-loop
Python
for day in range(1, 8):
distance = 3 + (day - 1) * 0.5
print(f"Day {day}: Run {distance:.1f} miles")
Output
Day 1: Run 3.0 miles
Day 2: Run 3.5 miles
Day 3: Run 4.0 miles
Day 4: Run 4.5 miles
Day 5: Run 5.0 miles
Day 6: Run 5.5 miles
Day 7: Run 6.0 miles
For Loops in Python – FAQs
What is the syntax of a for loop in Python?
The syntax of a for loop in Python is straightforward. It iterates over a sequence (like a list, tuple, string, etc.) and executes the block of code inside the loop for each element in the sequence.
for item in sequence:
# Code block to execute
How to iterate with an index in a for loop in Python?
You can use the ‘enumerate()’ function to iterate over a sequence and retrieve both the index and the value of each element.
for index, item in enumerate(sequence):
# Use index and item inside the loop
Can you provide examples of for loops in Python?
Sure! Here are some examples of for loops in Python:
# Example 1: Iterating over a list
fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
for fruit in fruits:
print(fruit)
# Example 2: Iterating over a string
for char in 'Python':
print(char)
# Example 3: Using enumerate to get index and value
for index, num in enumerate([10, 20, 30]):
print(f'Index {index}: {num}')
# Example 4: Iterating over a dictionary
person = {'name': 'John', 'age': 30}
for key, value in person.items():
print(f'{key}: {value}')
How to write a for loop in Python?
To write a for loop, specify the variable that will hold each item from the sequence (‘item’ in the examples above), followed by the keyword in and the sequence itself (‘sequence’ in the examples).
# Basic syntax
for item in sequence:
# Code block to execute
How to use for loops in Python?
For loops are used to iterate over sequences (like lists, tuples, strings, dictionaries) and perform operations on each element or key-value pair. They are fundamental for iterating and processing data in Python.
# Example: Calculating sum of numbers in a list
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
total = 0
for num in numbers:
total += num
print(f'Total sum: {total}')
Please Login to comment...