Minimum steps to reach target by a Knight | Set 1
Last Updated :
09 May, 2024
Given a square chessboard of N x N size, the position of the Knight and the position of a target are given. We need to find out the minimum steps a Knight will take to reach the target position.
Examples:
Input:
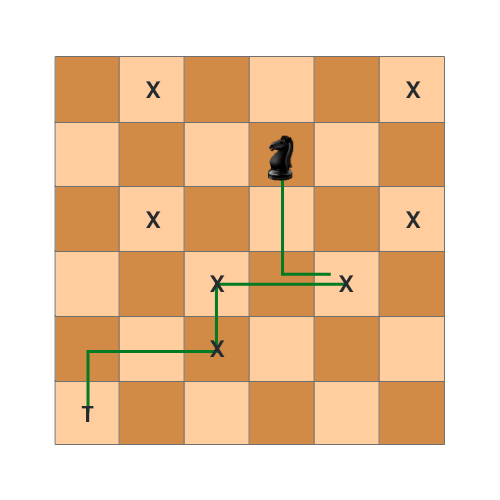
Knight
knightPosition: (1, 3) , targetPosition: (5, 0)
Output: 3
Explanation: In above diagram Knight takes 3 step to reach
from (1, 3) to (5, 0)
(1, 3) -> (3, 4) -> (4, 2) -> (5, 0)
Minimum steps to reach the target by a Knight using BFS:
To solve the problem follow the below idea:
This problem can be seen as the shortest path in an unweighted graph. Therefore, BFS is an appropriate algorithm to solve this problem.
Try all 8 possible positions where a Knight can reach from its position. If the reachable position is not already visited and is inside the board, push this state into the queue with a distance 1 more than its parent state. During the BFS traversal, if the current position is target position then return the distance of the target position.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// structure for storing a cell's data
struct cell {
int x, y;
int dis;
cell() {}
cell(int x, int y, int dis)
: x(x)
, y(y)
, dis(dis)
{
}
};
// Utility method returns true if (x, y) lies
// inside Board
bool isInside(int x, int y, int N)
{
if (x >= 1 && x <= N && y >= 1 && y <= N)
return true;
return false;
}
// Method returns minimum step
// to reach target position
int minStepToReachTarget(int knightPos[], int targetPos[],
int N)
{
// x and y direction, where a knight can move
int dx[] = { -2, -1, 1, 2, -2, -1, 1, 2 };
int dy[] = { -1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1 };
// queue for storing states of knight in board
queue<cell> q;
// push starting position of knight with 0 distance
q.push(cell(knightPos[0], knightPos[1], 0));
cell t;
int x, y;
bool visit[N + 1][N + 1];
// make all cell unvisited
memset(visit, false, sizeof(visit));
// visit starting state
visit[knightPos[0]][knightPos[1]] = true;
// loop until we have one element in queue
while (!q.empty()) {
t = q.front();
q.pop();
// if current cell is equal to target cell,
// return its distance
if (t.x == targetPos[0] && t.y == targetPos[1])
return t.dis;
// loop for all reachable states
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
x = t.x + dx[i];
y = t.y + dy[i];
// If reachable state is not yet visited and
// inside board, push that state into queue
if (isInside(x, y, N) && !visit[x][y]) {
visit[x][y] = true;
q.push(cell(x, y, t.dis + 1));
}
}
}
// If no valid path found, return -1
return -1;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int N = 30;
int knightPos[] = { 1, 1 };
int targetPos[] = { 30, 30 };
// Function call
cout << minStepToReachTarget(knightPos, targetPos, N);
return 0;
}
// Java program to find minimum steps to reach to
// specific cell in minimum moves by Knight
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Java program to find minimum steps to reach to
// specific cell in minimum moves by Knight
public class GFG {
// Class for storing a cell's data
static class cell {
int x, y;
int dis;
public cell(int x, int y, int dis)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.dis = dis;
}
}
// Utility method returns true if (x, y) lies
// inside Board
static boolean isInside(int x, int y, int N)
{
if (x >= 1 && x <= N && y >= 1 && y <= N)
return true;
return false;
}
// Method returns minimum step
// to reach target position
static int minStepToReachTarget(int knightPos[],
int targetPos[], int N)
{
// x and y direction, where a knight can move
int dx[] = { -2, -1, 1, 2, -2, -1, 1, 2 };
int dy[] = { -1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1 };
// queue for storing states of knight in board
Queue<cell> q = new LinkedList<>();
// push starting position of knight with 0 distance
q.add(new cell(knightPos[0], knightPos[1], 0));
cell t;
int x, y;
boolean visit[][] = new boolean
[N + 1][N + 1]; // default initialized to false
// visit starting state
visit[knightPos[0]][knightPos[1]] = true;
// loop until we have one element in queue
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
t = q.poll();
// if current cell is equal to target cell,
// return its distance
if (t.x == targetPos[0] && t.y == targetPos[1])
return t.dis;
// loop for all reachable states
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
x = t.x + dx[i];
y = t.y + dy[i];
// If reachable state is not yet visited and
// inside board, push that state into queue
if (isInside(x, y, N) && !visit[x][y]) {
visit[x][y] = true;
q.add(new cell(x, y, t.dis + 1));
}
}
}
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 30;
int knightPos[] = { 1, 1 };
int targetPos[] = { 30, 30 };
// Function call
System.out.println(
minStepToReachTarget(knightPos, targetPos, N));
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
# Python3 code to find minimum steps to reach
# to specific cell in minimum moves by Knight
class cell:
def __init__(self, x=0, y=0, dist=0):
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.dist = dist
# checks whether given position is
# inside the board
def isInside(x, y, N):
if (x >= 1 and x <= N and
y >= 1 and y <= N):
return True
return False
# Method returns minimum step to reach
# target position
def minStepToReachTarget(knightpos,
targetpos, N):
# all possible movements for the knight
dx = [2, 2, -2, -2, 1, 1, -1, -1]
dy = [1, -1, 1, -1, 2, -2, 2, -2]
queue = []
# push starting position of knight
# with 0 distance
queue.append(cell(knightpos[0], knightpos[1], 0))
# make all cell unvisited
visited = [[False for i in range(N + 1)]
for j in range(N + 1)]
# visit starting state
visited[knightpos[0]][knightpos[1]] = True
# loop until we have one element in queue
while(len(queue) > 0):
t = queue[0]
queue.pop(0)
# if current cell is equal to target
# cell, return its distance
if(t.x == targetpos[0] and
t.y == targetpos[1]):
return t.dist
# iterate for all reachable states
for i in range(8):
x = t.x + dx[i]
y = t.y + dy[i]
if(isInside(x, y, N) and not visited[x][y]):
visited[x][y] = True
queue.append(cell(x, y, t.dist + 1))
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
N = 30
knightpos = [1, 1]
targetpos = [30, 30]
# Function call
print(minStepToReachTarget(knightpos,
targetpos, N))
# This code is contributed by
# Kaustav kumar Chanda
// C# program to find minimum steps to reach to
// specific cell in minimum moves by Knight
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// Class for storing a cell's data
public class cell {
public int x, y;
public int dis;
public cell(int x, int y, int dis)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.dis = dis;
}
}
// Utility method returns true
// if (x, y) lies inside Board
static bool isInside(int x, int y, int N)
{
if (x >= 1 && x <= N && y >= 1 && y <= N)
return true;
return false;
}
// Method returns minimum step
// to reach target position
static int minStepToReachTarget(int[] knightPos,
int[] targetPos, int N)
{
// x and y direction, where a knight can move
int[] dx = { -2, -1, 1, 2, -2, -1, 1, 2 };
int[] dy = { -1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1 };
// queue for storing states of knight in board
Queue<cell> q = new Queue<cell>();
// push starting position of knight with 0 distance
q.Enqueue(new cell(knightPos[0], knightPos[1], 0));
cell t;
int x, y;
bool[, ] visit = new bool[N + 1, N + 1];
// make all cell unvisited
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++)
visit[i, j] = false;
// visit starting state
visit[knightPos[0], knightPos[1]] = true;
// loop until we have one element in queue
while (q.Count != 0) {
t = q.Peek();
q.Dequeue();
// if current cell is equal to target cell,
// return its distance
if (t.x == targetPos[0] && t.y == targetPos[1])
return t.dis;
// loop for all reachable states
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
x = t.x + dx[i];
y = t.y + dy[i];
// If reachable state is not yet visited and
// inside board, push that state into queue
if (isInside(x, y, N) && !visit[x, y]) {
visit[x, y] = true;
q.Enqueue(new cell(x, y, t.dis + 1));
}
}
}
return int.MaxValue;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 30;
int[] knightPos = { 1, 1 };
int[] targetPos = { 30, 30 };
// Function call
Console.WriteLine(
minStepToReachTarget(knightPos, targetPos, N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
<script>
// Javascript program to find minimum steps to reach to
// specific cell in minimum moves by Knight
// Class for storing a cell's data
class cell
{
constructor(x,y,dis)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.dis = dis;
}
}
// Utility method returns true if (x, y) lies
// inside Board
function isInside(x,y,N)
{
if (x >= 1 && x <= N && y >= 1 && y <= N)
return true;
return false;
}
// Method returns minimum step
// to reach target position
function minStepToReachTarget(knightPos,targetPos,N)
{
// x and y direction, where a knight can move
let dx = [ -2, -1, 1, 2, -2, -1, 1, 2 ];
let dy = [ -1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1 ];
// queue for storing states of knight in board
let q = [];
// push starting position of knight with 0 distance
q.push(new cell(knightPos[0], knightPos[1], 0));
let t;
let x, y;
let visit = new Array(N + 1);
// make all cell unvisited
for (let i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
visit[i]=new Array(N+1);
for (let j = 1; j <= N; j++)
visit[i][j] = false;
}
// visit starting state
visit[knightPos[0]][knightPos[1]] = true;
// loop until we have one element in queue
while (q.length!=0) {
t = q.shift();
// if current cell is equal to target cell,
// return its distance
if (t.x == targetPos[0] && t.y == targetPos[1])
return t.dis;
// loop for all reachable states
for (let i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
x = t.x + dx[i];
y = t.y + dy[i];
// If reachable state is not yet visited and
// inside board, push that state into queue
if (isInside(x, y, N) && !visit[x][y]) {
visit[x][y] = true;
q.push(new cell(x, y, t.dis + 1));
}
}
}
return Number.MAX_VALUE;
}
// Driver code
let N = 30;
let knightPos=[1,1];
let targetPos=[30,30];
document.write(
minStepToReachTarget(
knightPos, targetPos, N));
// This code is contributed by rag2127
</script>
Time complexity: O(N2). In the worst case, all the cells will be visited
Auxiliary Space: O(N2). The nodes are stored in a queue.
Please Login to comment...